Rubber Processability Improvement Technologies — Silica Dispersants
Introduction
The tire manufacturing process typically includes mixing natural or synthetic rubber with various compounding agents—such as reinforcing fillers, processing aids, and vulcanizing agents—followed by vulcanization (curing) and molding. In recent years, there has been an increase in the inclusion of silica (white carbon) as a reinforcing filler to further lower fuel consumption and enhance grip on wet road surfaces.
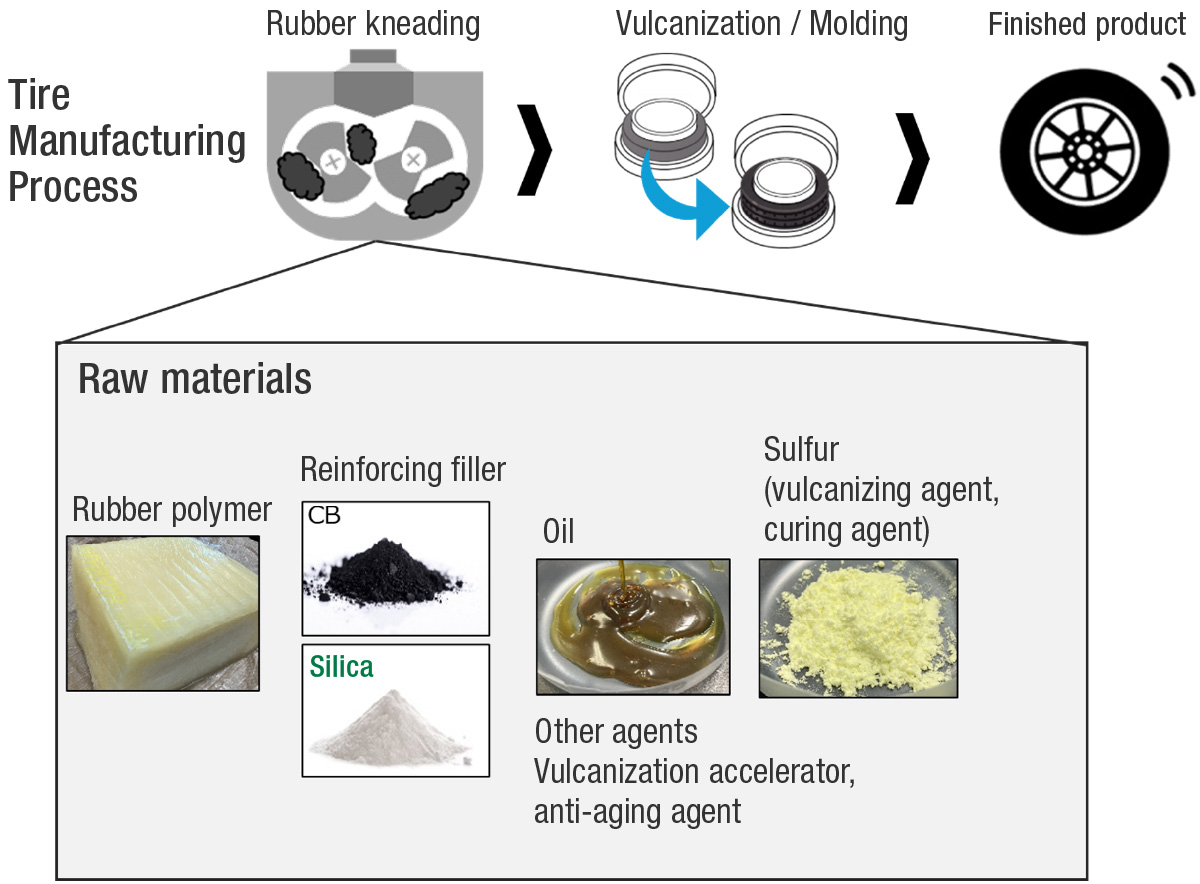
Representative processing aids
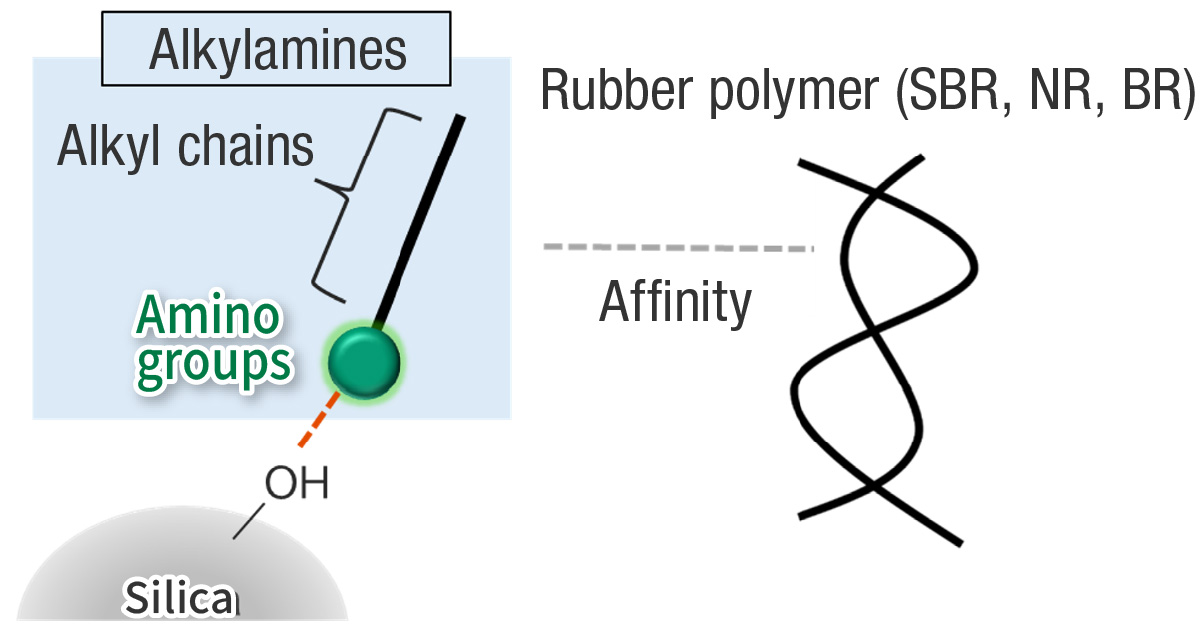
Hydrophilic functional groups (Si-OH) on the surface of silica hamper its dispersion in the hydrophobic rubber, viscosity during mixing and reduced processability. To address this issue, processing aids are sometimes used. Metal soaps are a well-known representative processing aid that enhance the flow of the rubber and thereby aid the overall mixing process. However, they are limited in terms of improving silica dispersion.
Application of Alkylamines as Silica Dispersant
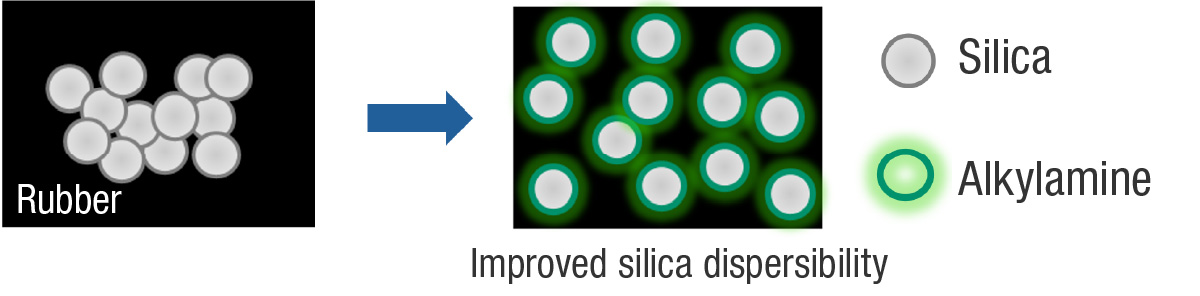
Due to a molecular structure featuring amino groups (-NR2) in their molecules, Alkylamines are suitable for use as processing aids, and silica dispersants in particular as they promote the dispersion of silica in rubber. This is due to alkylamines’ strong adsorption to silica through their amino groups. Given the alkyl chains affinity with rubber, they also have the potential to improve the compatibility of silica and various polymers.
The Company selects alkylamine derivatives based on suitability for use as processing aids while advancing the development of silica dispersants. Our silica dispersants help improve rubber’s overall processability and thus manufacturing productivity.