Anti-Sticking Agents
Introduction
In general, “The Anti-Sticking Agent” stands for the agent which reduce or avoid sticking on the surface of un-vulcanized rubber. This agent is necessary for you to pile up the un-vulcanized rubber for its tentative stock for few days. Utilizing surfactants, anti-sticking agents employ technology to evenly apply anti-sticking elements on hydrophobic rubber surfaces. The technologies for rubber surface modification are described below.
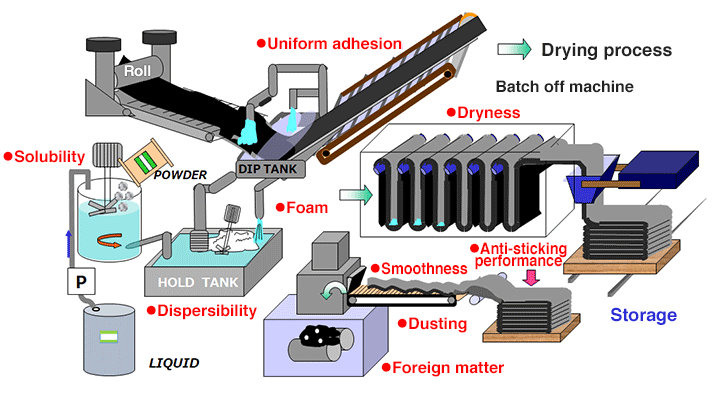
Anti-Sticking Agent Treatment Process
The anti-sticking agent is dissolved and dispersed in water to create the treatment solution, which is then used to submerge the rolled rubber.
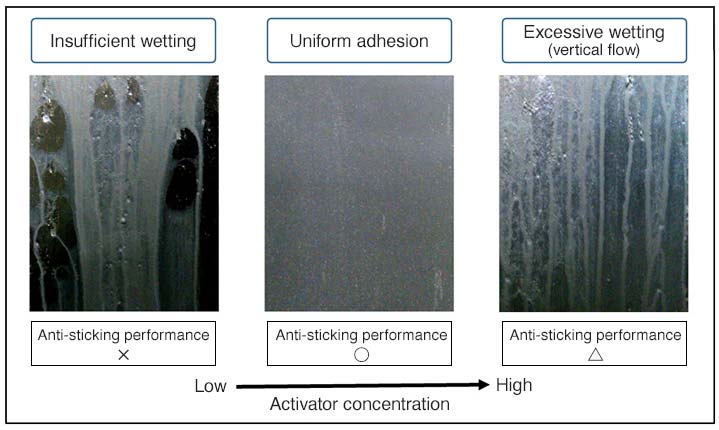
Rubber Surface Condition after Dipping Treatment
The variety and concentration of surfactant in the anti-sticking agent and rubber type affect the treated surface’s surface condition, and the main challenge is achieving uniform adherence as seen in the center picture.

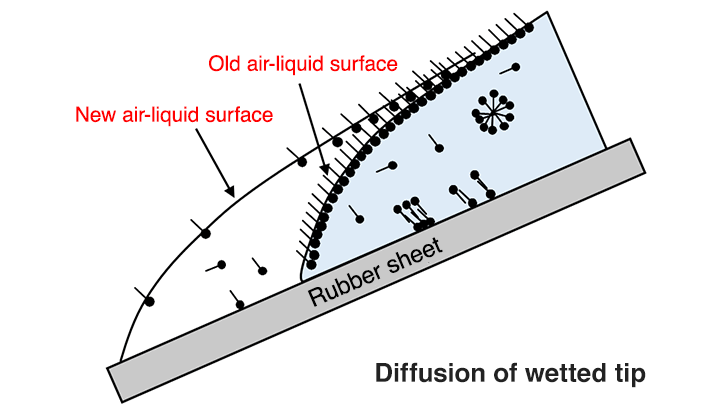
Wetting Dynamic Behavior
The figure illustrates how the wetting tip diffuses when the treated liquid is applied to the rubber surface. For uniform adherence, we found that the activator’s quick adsorption on the new air-liquid surface was effective.
We measured the surface tension of different surfactants as they changed over time using the maximum bubble pressure method, focusing on dynamic surface tension as an indicator to assess the adsorption rate of the active agent on the wetting tip.
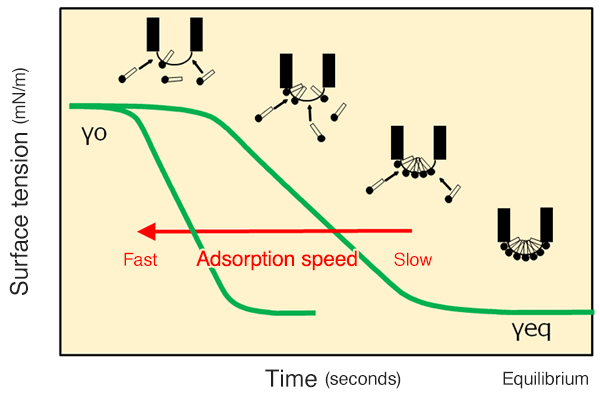
Fig. 1 Conceptual diagram of dynamic surface tension
Five levels of evaluation were used to assess the adherence of surfactants on rubber surfaces at varying adsorption speeds. Plotting the relationship between adhesion and adsorption speed revealed some association between the two.
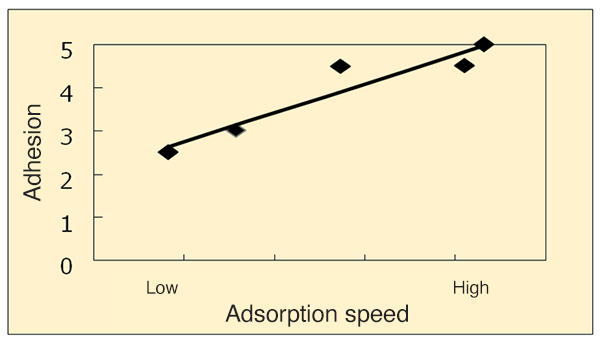
Fig. 2 Relationship between adsorption speed and adhesion
This technology has shown that an active agent with the same surface tension but a higher adsorption speed is very effective in adhering to rubber. Previously, we based the selection of surfactants for uniform adhesion in the development of anti-sticking agents on surface tension measured under equilibrium conditions.
This technology has been used for a variety of anti-sticking applications, including polymer anti-sticking agents, in addition to powder-type anti-sticking agents.
References
- 金子行裕 第5章 界面活性剤 ぬれ技術ハンドブック; テクノシステム : 東京, 2001; pp221
- 田嶋和夫 界面活性剤評価・試験法; 日本油化学会 : 東京, 2002; pp160