Functional Polymer Design Technology
Cationic Cellulose Functions
Cationic cellulose is a versatile substance used in cosmetics and toiletries with particular application in shampoo as a conditioning agent.
Cationic Cellulose Structural Formula
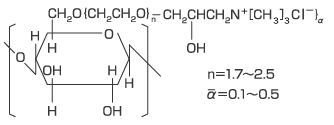
The LEOGARD series is produced by adding the cationic agent glycidyltrimethylaminium chloride to hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC). This formulation has a molecular weight of 0.15 to 1.5 million, resulting in a cationic base induction rate of approximately 0.1 to 0.5 per unit of anhydroglucose (about 0.5 to 2.0 nitrogen content conversions).
The relationship between the LEOGARD series’ nitrogen content and the viscosity of the aqueous solution
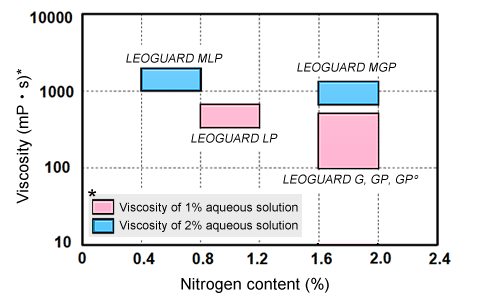
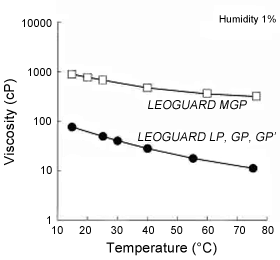
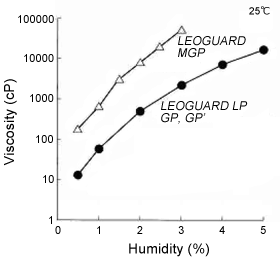
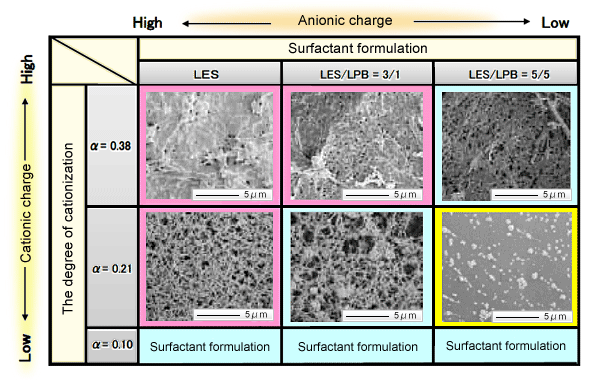
Cationic cellulose forms water-insoluble complex salts through the interaction of anionic surfactants and amphoteric surfactants, both of which are ingredients of shampoo. These complex salts are absorbed by the hair for superior conditioning effectiveness. The form taken by the complex salts changes depending on the degree of cationization of the cellulose and the type of surfactant. This morphological disparity is said to be closely related to conditioning effectiveness.
Observation of complex salt formations due to catonization of cellulose and type of surfactant (dried at the CO2 supercritical point)
According to Lion documents presented at the 19th Symposium
for Engineers in the Colioid and Surface Industry. 2002